SEO Spider Guide
If with the SEO Checker you can analyze in detail the degree of optimization of a single web page, thanks to the SEO Spider it is possible to scan all the pages of a site, because it behaves and analyzes the pages exactly as if was the crawler of a search engine.
To do this, simply access its dashboard from the menu on the left!
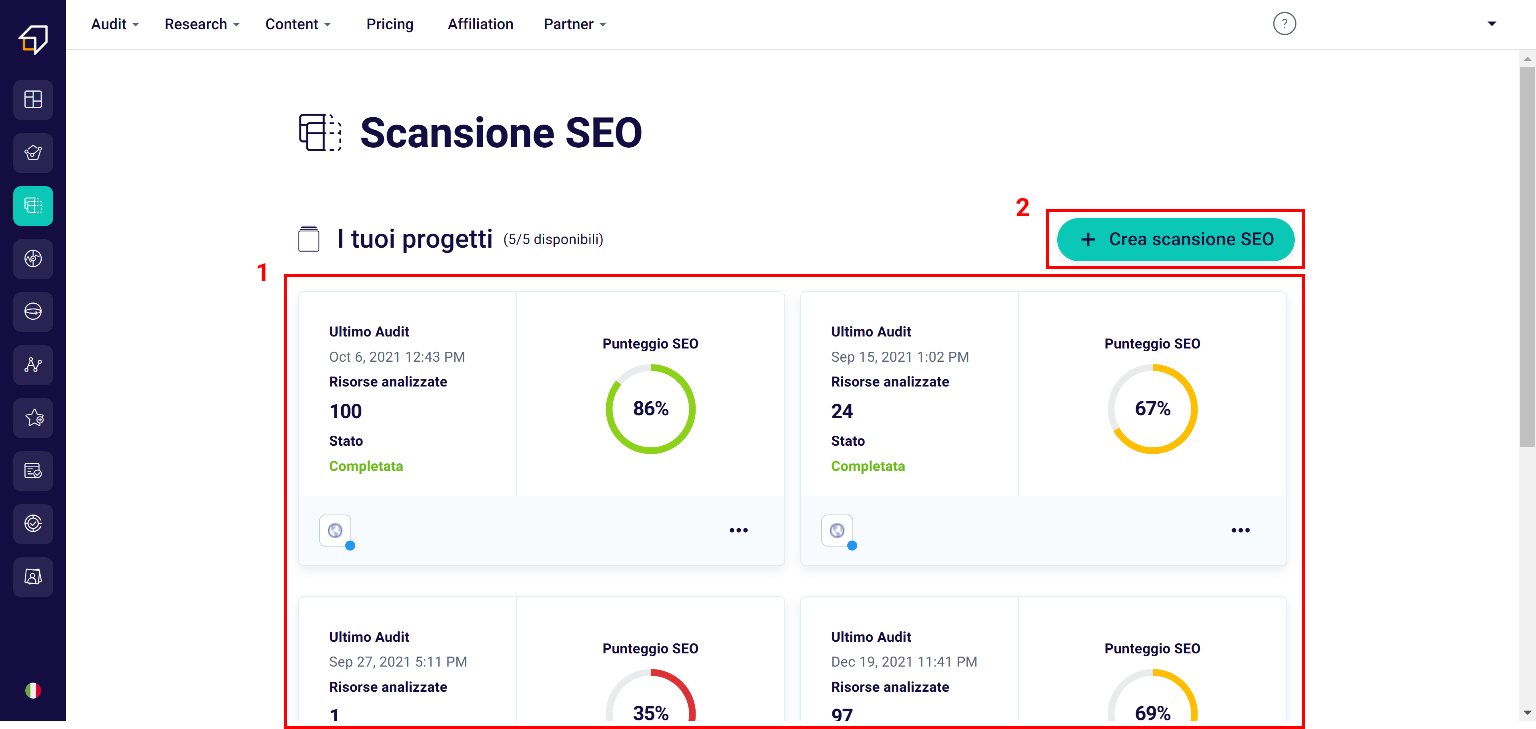
Within the page that appears, in fact, you can decide whether to use one of your existing SEO projects (1), or create a new scan (new SEO project) (2).
We have written a very complete guide on creating SEO projects and if you have not read it yet, we recommend that you do so before proceeding with this reading!
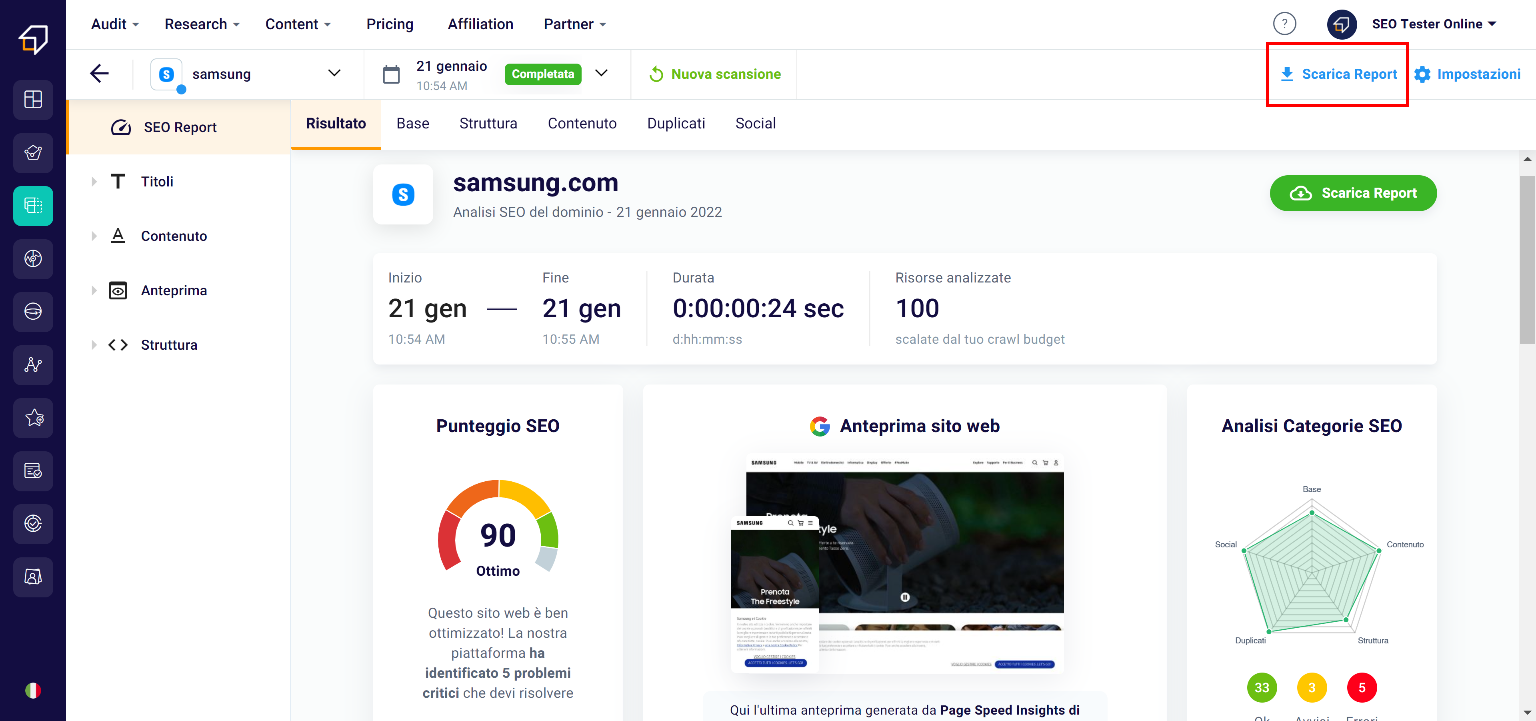
Result
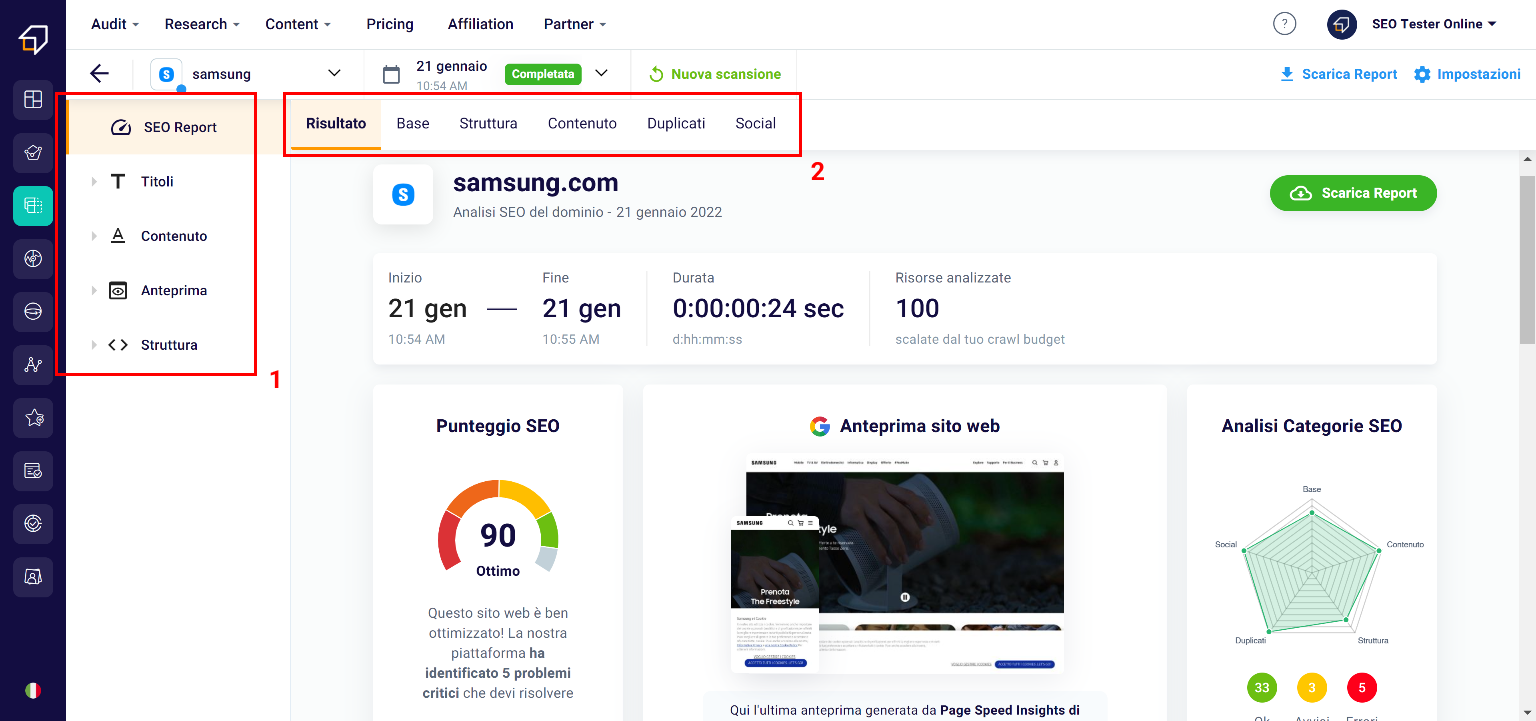
After creating a new Project, or selecting one of the existing ones, in a few seconds you will get the scan result, an overview with which you can evaluate the overall SEO performance score and guess at a glance which aspects should be improved.
To go deeper into the analysis, you can use two menus:
- the side one (1) which will allow you to easily navigate between the various elements analyzed;
- the upper one (2) thanks to which you can study the 5 SEO Categories: Basic, Structure, Content, Duplicates and Social.
Let’s start from the Base!
Base
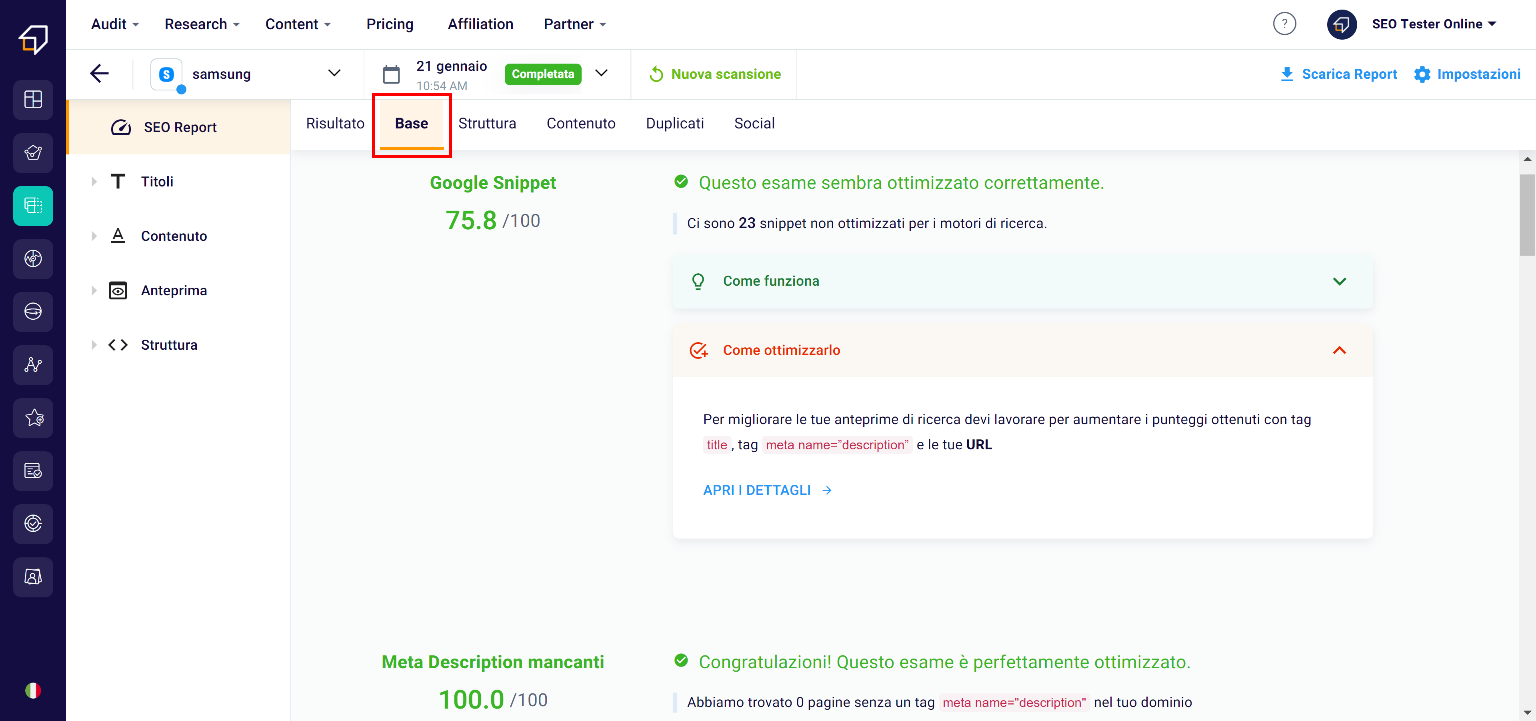
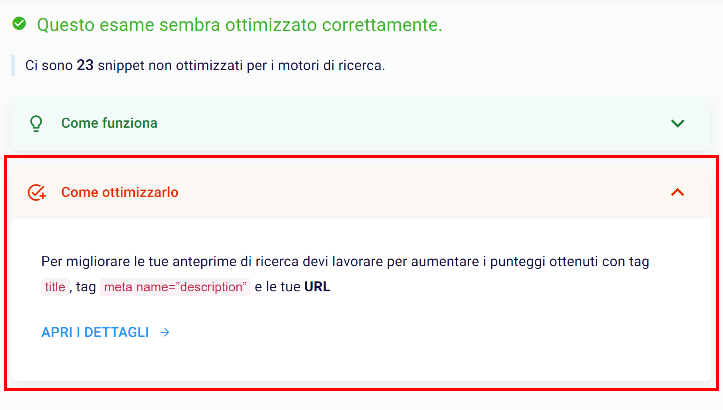
After viewing the generic information in the “Result” section, clicking on “Base” you will be able to view the elements of the code that have been optimized.
In particular, let’s talk about snippets, meta descriptions, titles, canonical tags etc.
In case of any critical issues, the SEO Spider will suggest the changes through the red section “How to solve it”.
Furthermore, by clicking on “Open details” you can study the anomalies more specifically!
Structure
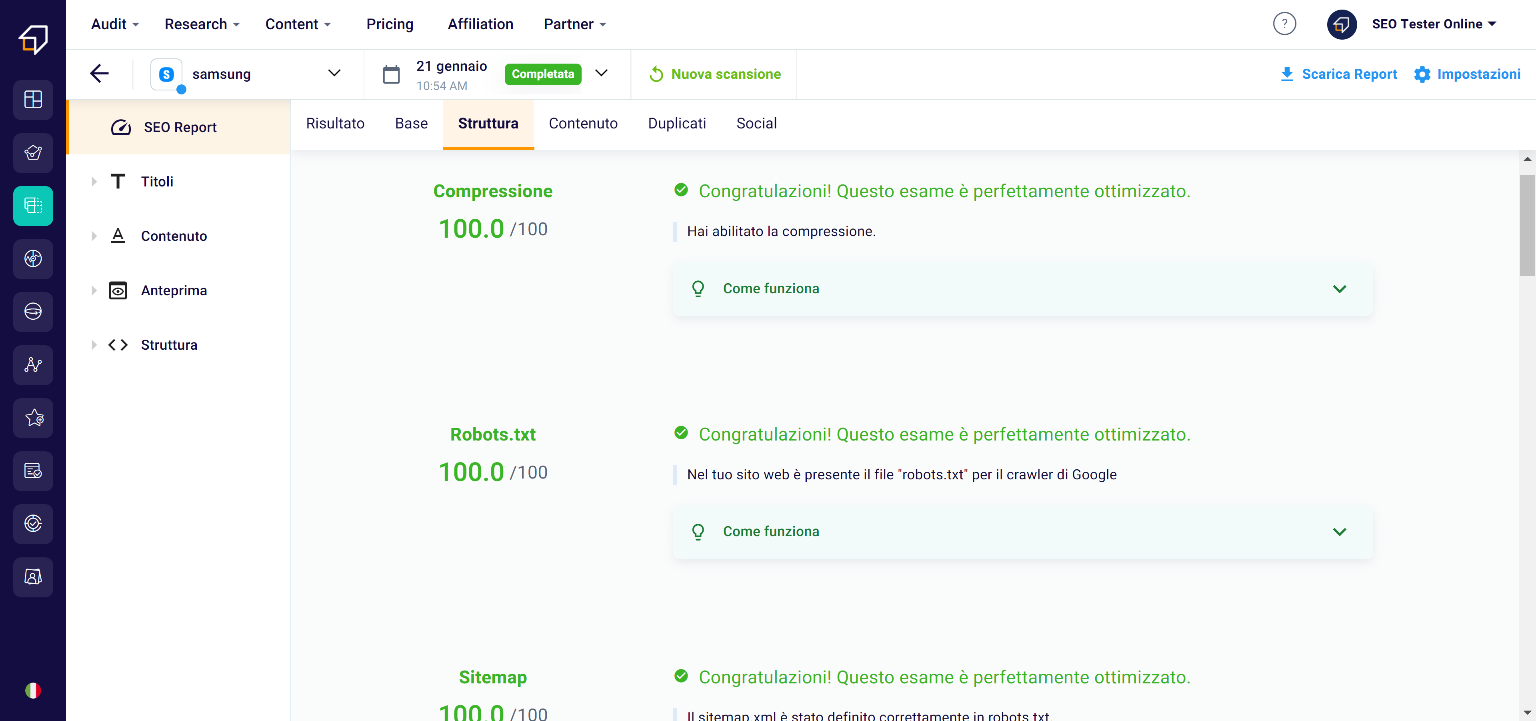
The “Structure” section, on the other hand, will list the results of the analysis of all the elements that make it easier for search engine crawlers to crawl.
Among the various parameters, for example, you can check if the website sitemap has been loaded correctly, if there are pages not found, or if the robots.txt file has been optimized correctly.
Also in this case, if there are any problems, the SEO Spider will suggest the interventions to be made thanks to the section “How to optimize it”.
Content
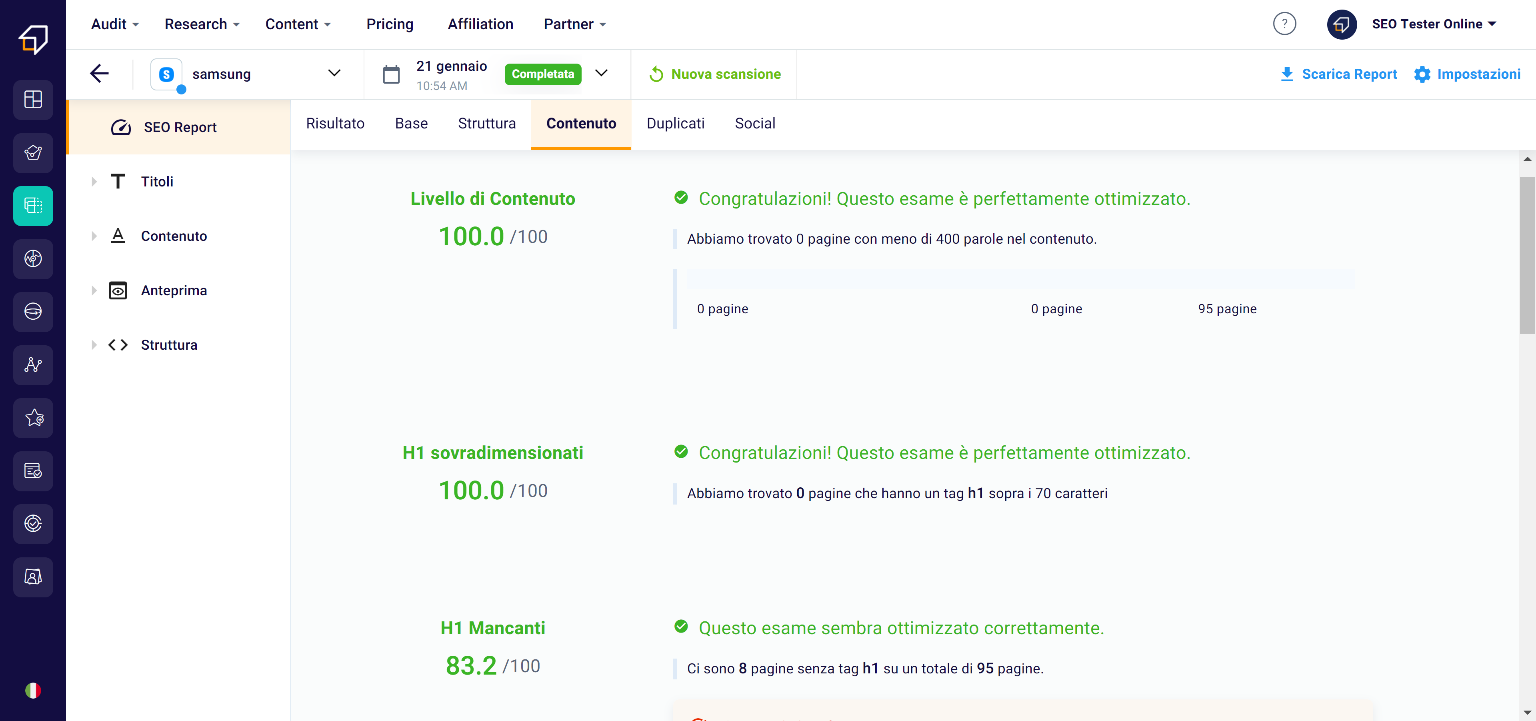
As you can guess from the title, this area of the tool is dedicated to content.
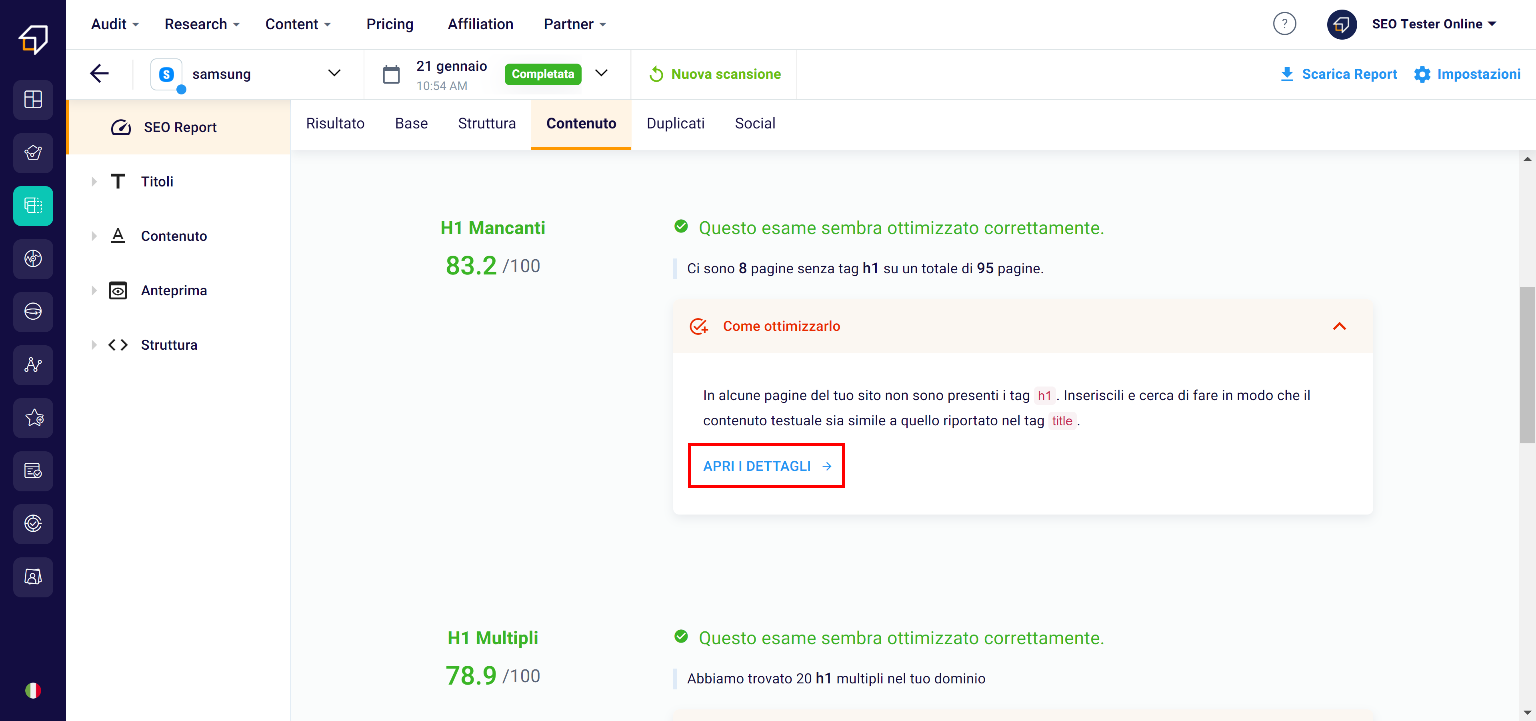
In fact, here you can check how many pages have the right elements inside them, if the h1 / 2/3 tags are the right size or if they are completely missing etc.
Always remember that in the “How to optimize it” area you can investigate the various critical issues by clicking on “Open details”.
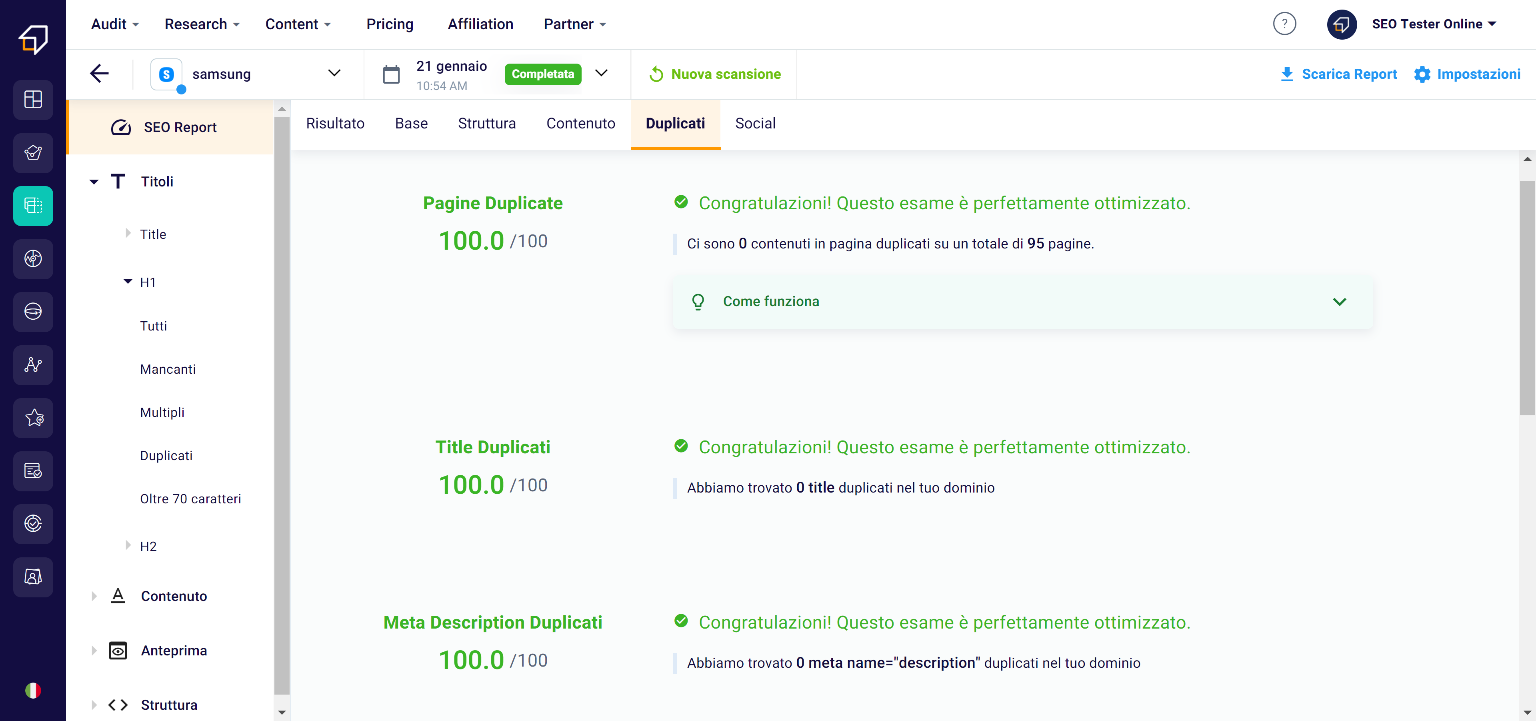
Duplicates
Duplicates on a website should always be avoided. In this section, in fact, you can make sure that there are no unnecessary copies on your site, including meta descriptions, titles or entire pages.
Unfortunately duplicate content could be penalized by search engines, so be very careful and make the most of this section to make sure that all the content on your website is exclusive and valuable.
Social
Thanks to the Social section you will be able to see the pages of your website for which the snippets and social cards have not been correctly set.
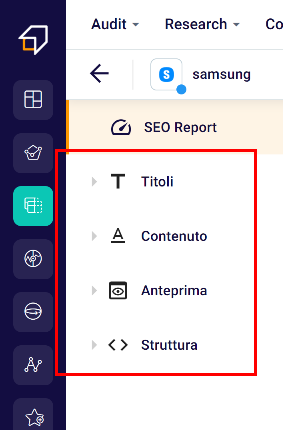
Now let’s move on to the side menu, which will allow you to navigate in a simple and intuitive way between the various elements analyzed by our SEO Spider.
As you can see, it is made up of 4 macro categories:
- Titles
- Content
- Preview
- Structure
Let’s find out together in more detail!
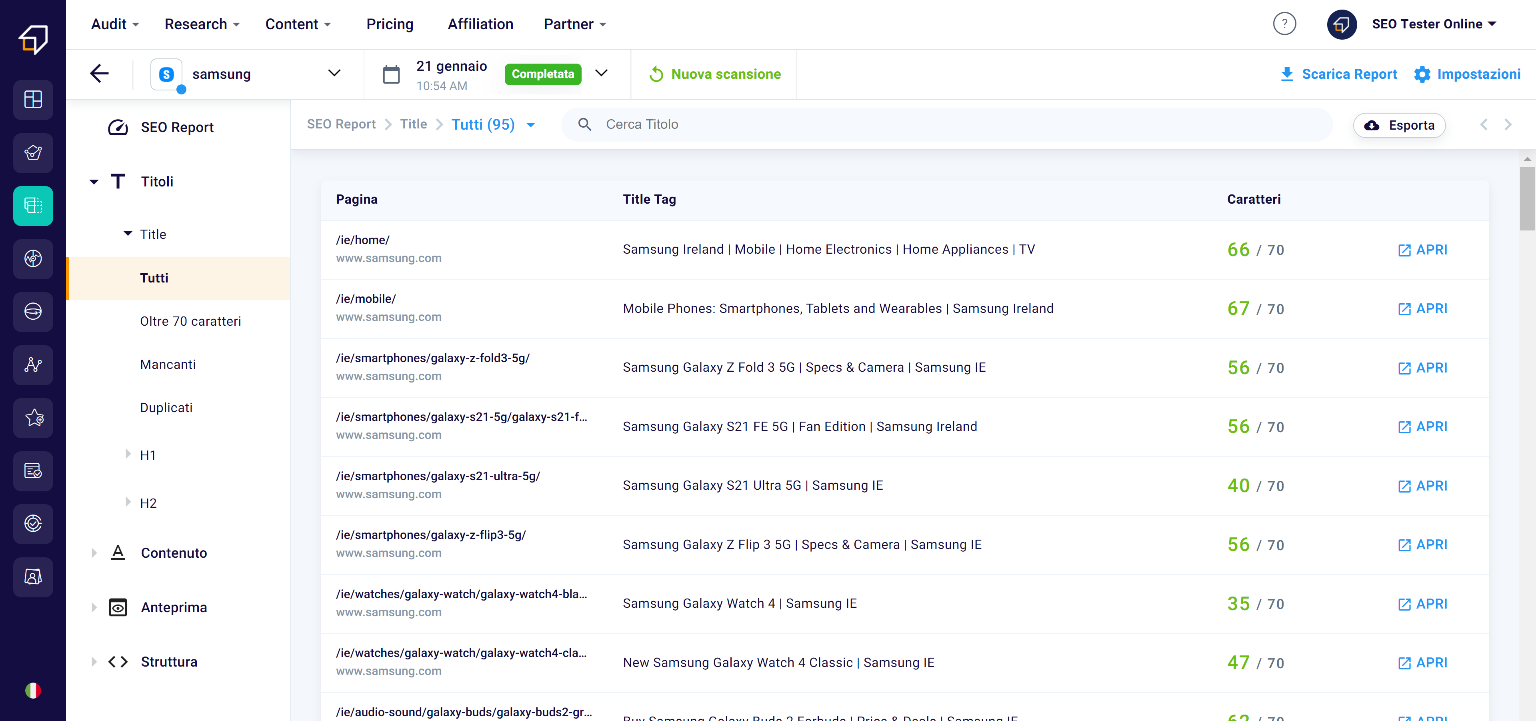
Title
The Title is that portion of text contained in the tag of the same name within the html code of the page and is the title that will appear, among other things, in the preview of the page when we find it on search engines.
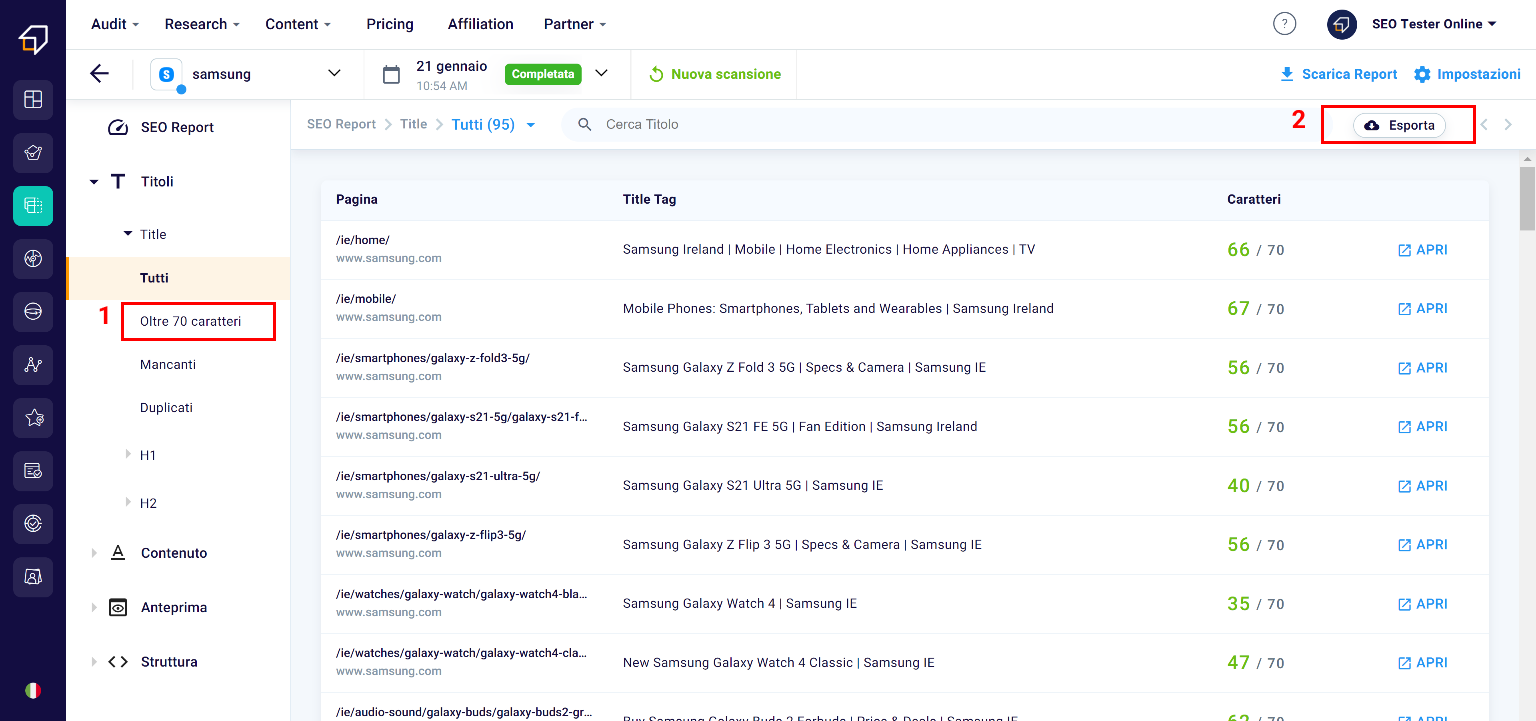
In this section you will have the possibility to filter them, for example in order to identify those that exceed the maximum size of 70 characters (1) (beyond which a title is cut) and export them to .xlsx files (2)
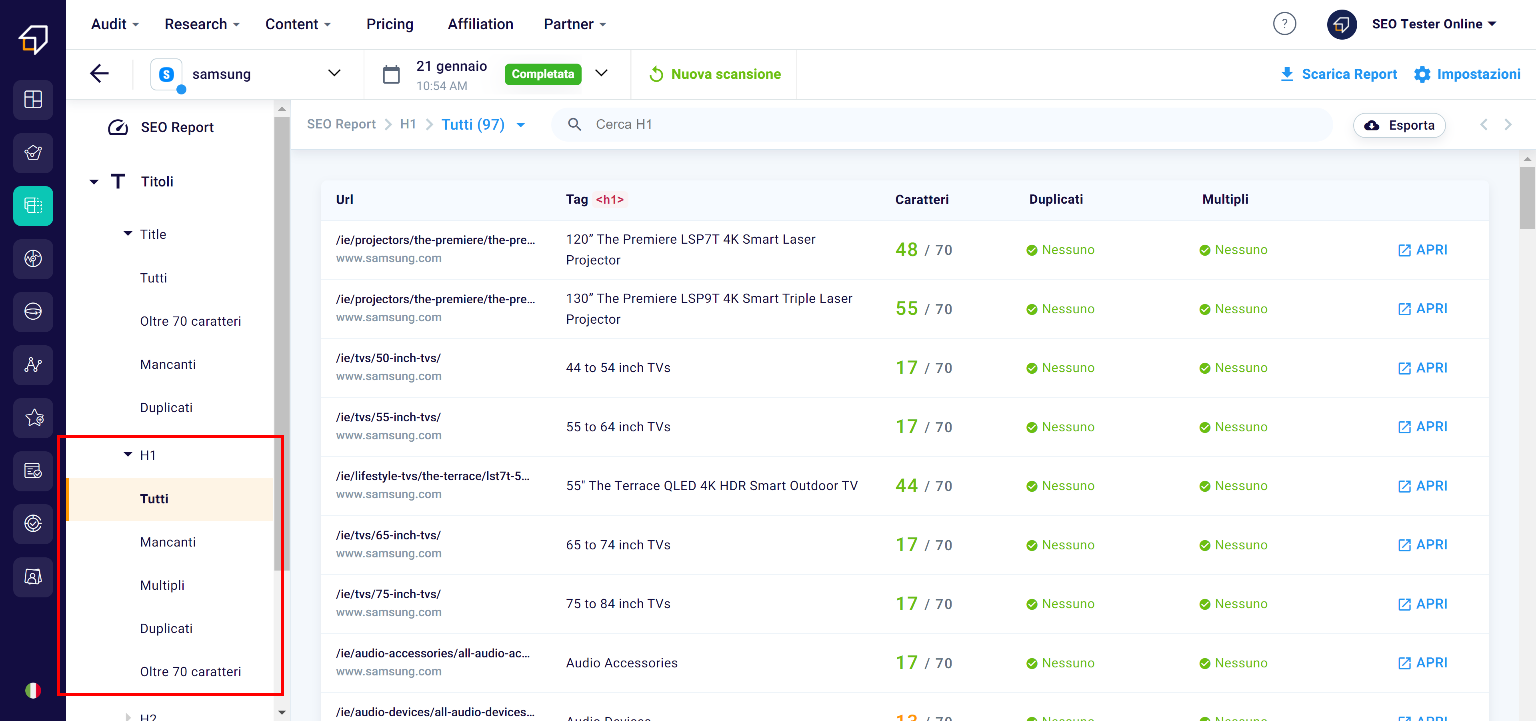
H1 and H2
H1 and H2, on the other hand, are titles of varying importance within the text and are used to give a hierarchy to the paragraphs.
In this case, you will be able to filter the titles by excessive size, missing ones or duplicates.
Plus, only in the case of H1s, you will be able to filter them by multiple titles. This is because normally, in case your page is not divided into sections, the best solution might be to enter only one H1 per page.
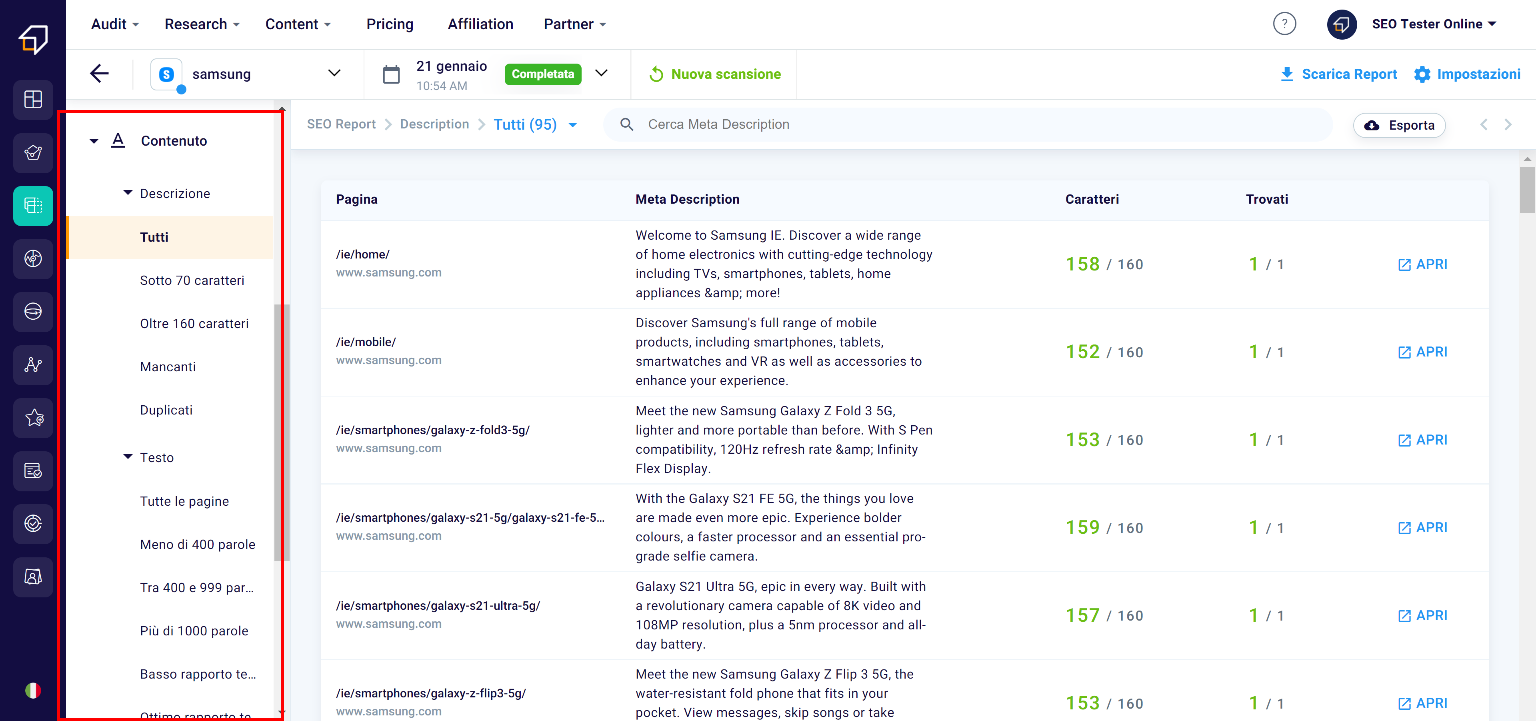
Content
As for the Content, you will be able to navigate between the descriptions (i.e. the descriptive text of the snippet), the titles, the images etc. in order to verify the dimensions and the correct configuration.
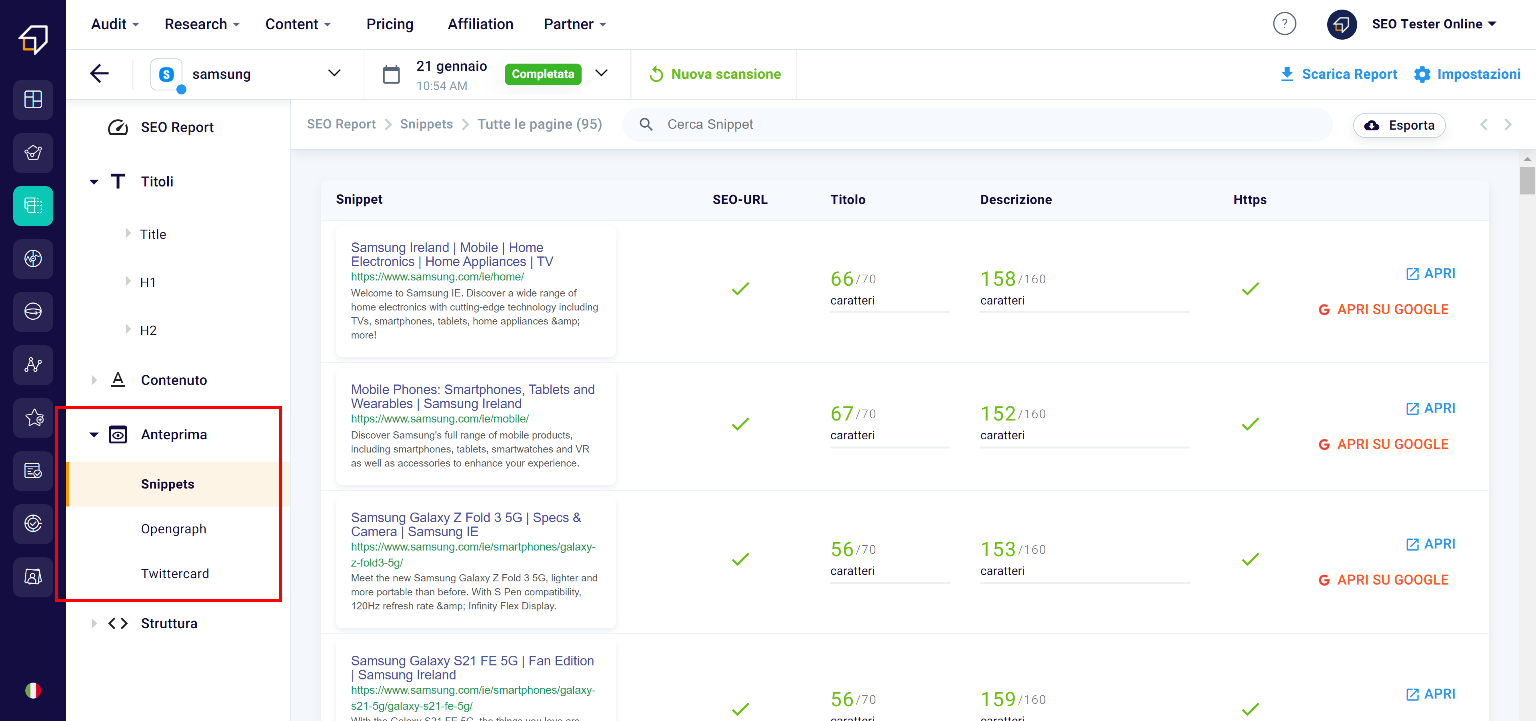
Preview
Under the macro-category “Preview” we find the sections “Snippets”, “Opengraph” and “Twitter Card”.
Let’s see them in more detail individually!
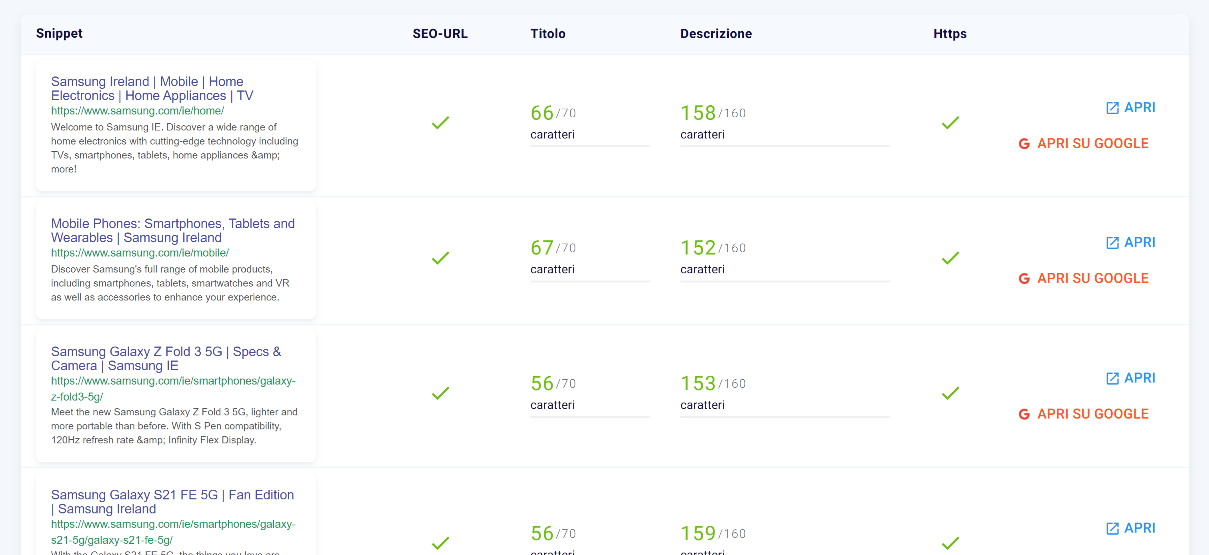
Google Snippets
The snippets are the previews of the pages that we find on the Google results page and include the title, the URL and a description.
Generally, search engines reward titles and descriptions with well-defined lengths, which you will be able to keep an eye on thanks to the SEO Spider, and tend to truncate too long texts contained in them for reasons of SERP design.
Opengraph and Twitter Card
The Opengraph and the Twitter Card are the equivalent of the snippets on Facebook and Twitter, or the structured preview of the page that appears when we link it on these social networks.
Now let’s move on to the fourth and last point of this menu: the Structure.
Structure
Structure is crucial from an SEO point of view. The more “easy” a site is to navigate, with simple paths for the crawler and the user, the more it will be rewarded by search engines.
Let’s see in detail the individual elements that make it up.
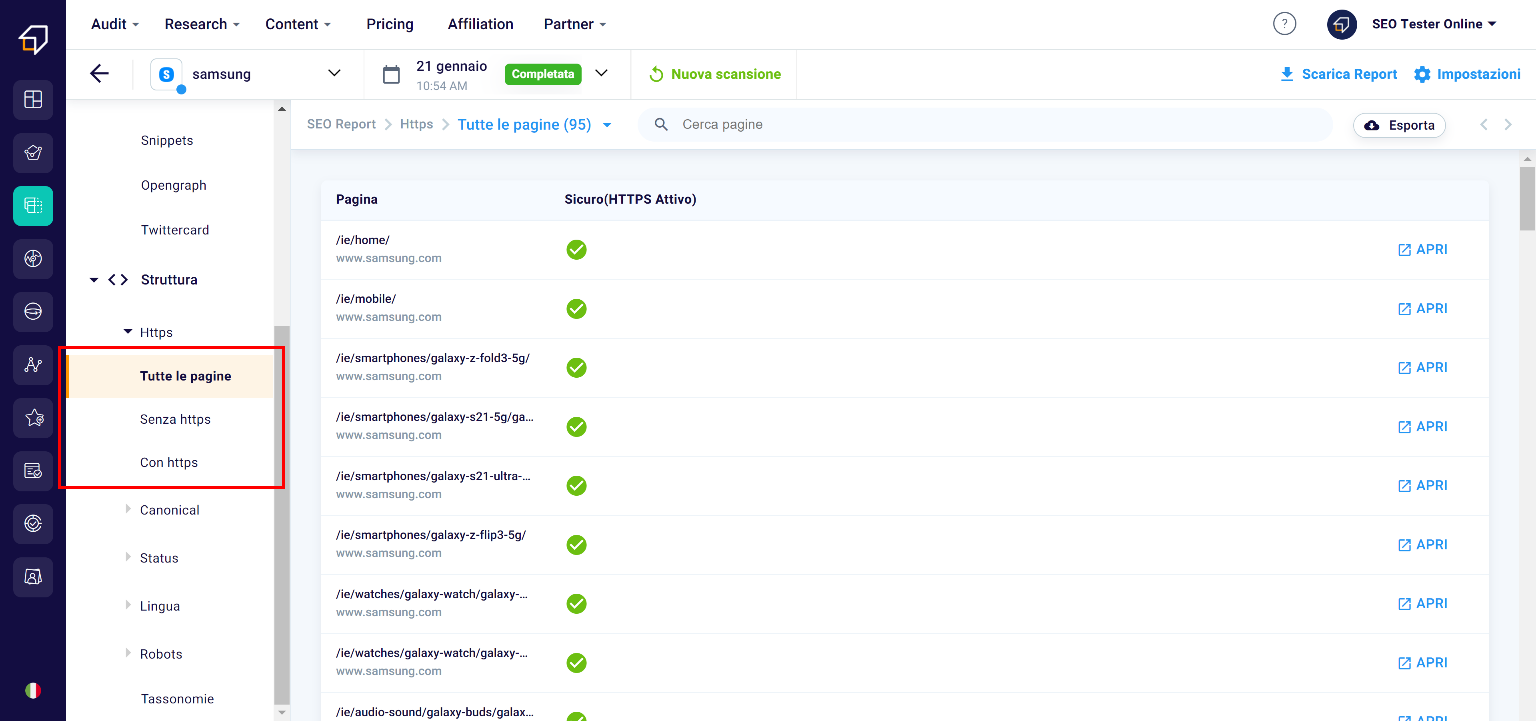
Https
Https is a security protocol whose absence, for some time, may not be frowned upon both by search engines (Chrome tends to classify these sites as “unsafe”), and by users ( especially if the security protocol is missing in a website on which personal data and / or payment data are entered, which could be more easily to the goods and to malicious subjects). To implement it on your site, you can follow this guide from Google.
In this section, you can filter pages according to two criteria – pages with https and without – and export the list. In this way, you can also avoid the presence of so-called “mixed contents” on your site, ie pages and resources with different protocols within the same site, a practice not well received by search engines.
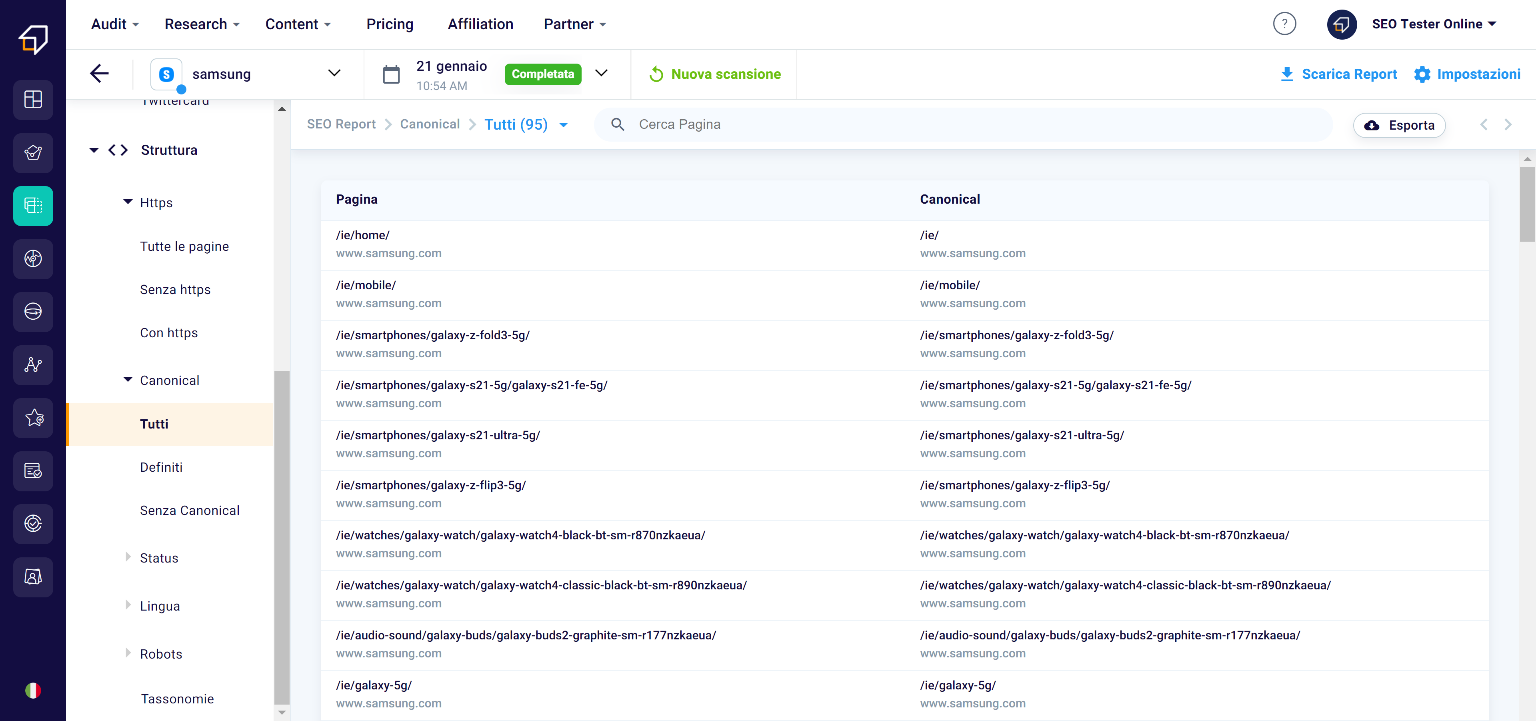
Canonical
The canonical attribute is very useful if our site has multiple pages with the same content (eg the description pages of a pair of shoes in its different color variations).
When we use this attribute on a page, we communicate to the search engine which page is to be considered the holder of the original content and which are simple variants.
In the event that canonical is necessary, but is not used, the crawler could consider all pages as duplicates, detecting the same content within them and ending up penalizing the positioning of the entire site.
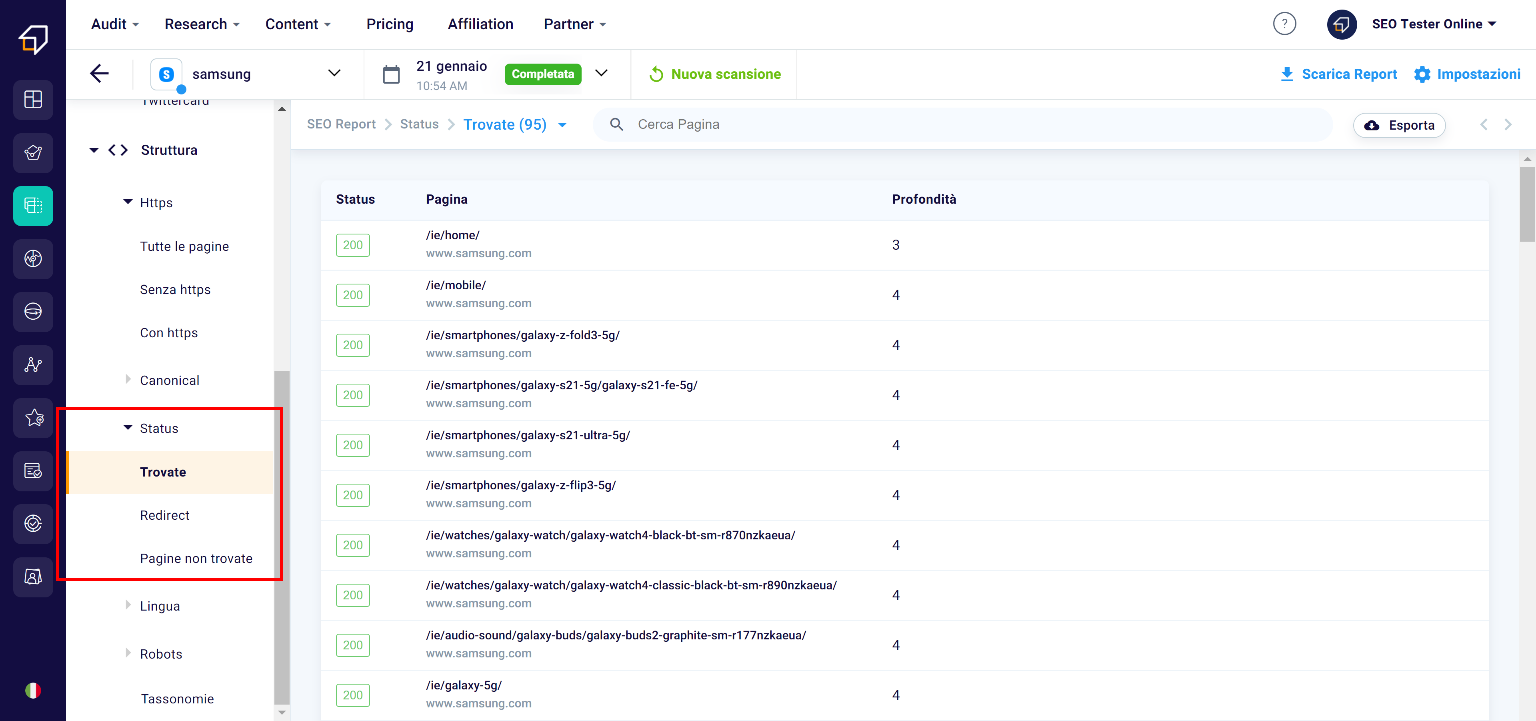
Status
The status is what the client (ie the user) receives from the server when it requests to view a certain web page via the http communication protocol.
These statuses can have different codes depending on the type of response.
HTTP status codes are divided into 5 “classes”:
- 100: informative responses;
- 200: successful answers;
- 300: redirect information;
- 400: client error responses;
- 500: Server error responses.
Within each of these classes, there are different codes that can be returned by the server and each has a specific and unique meaning.
Language
Under Language, thanks to the “filter” function, you can view which pages do not have the hreflang or x-default attributes and export them to file.
When we are in the presence of a multilingual site, it is good practice to insert on each page the link to its equivalents in each language using the <link hreflang> attribute.
The x-default attribute, on the other hand, indicates which “version” the search engine must consider as default and show when the site visitor comes from a region whose language is not present on the site.
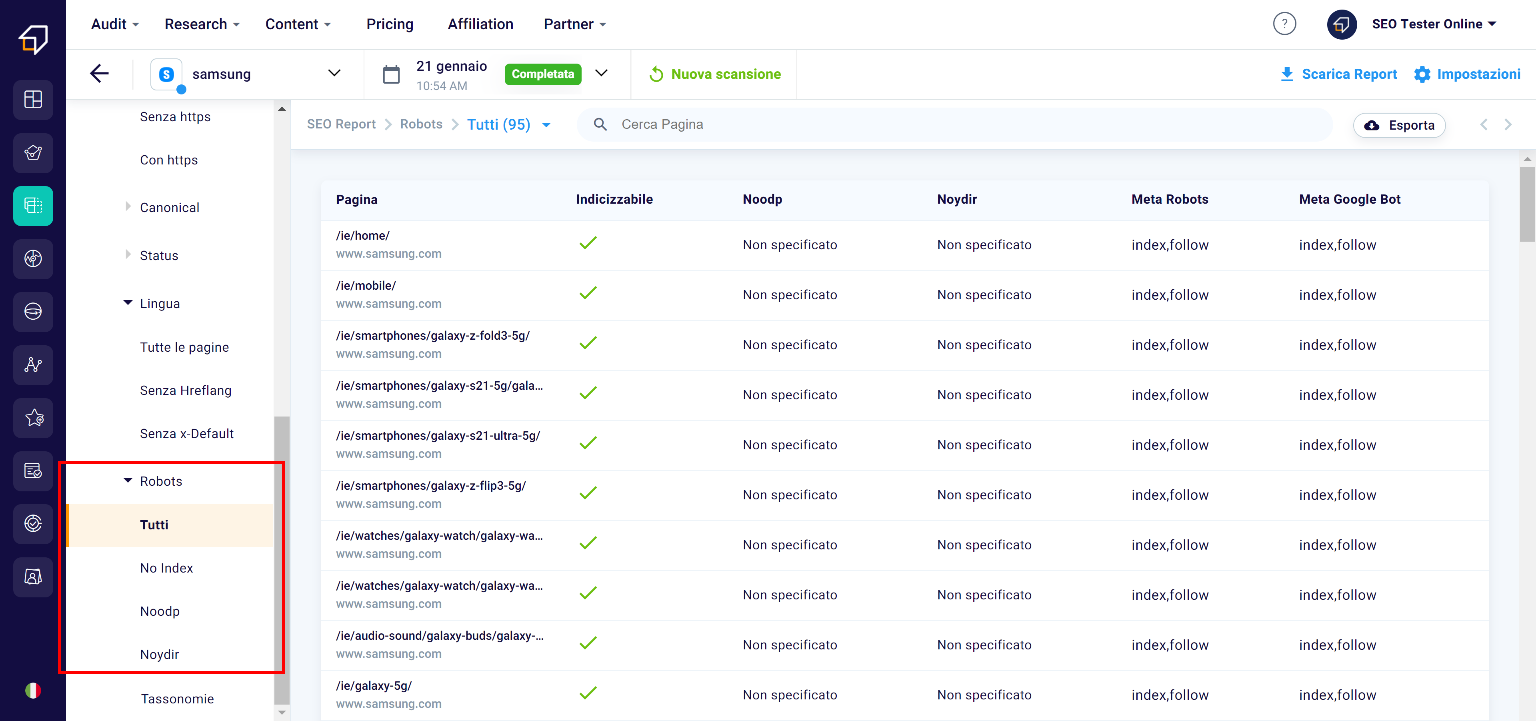
Robots
The robots.txt file within the site contains the “instructions” to be given to the crawler about the pages it must explore, how to do it and which ones it should ignore.
Here you will have the opportunity to view which pages in the robots.txt file have the noindex attribute – which invites you to block the indexing of that page to search engines – noodp and noydir, which instead suggest to search engine robots not use the site information found in the Yahoo and Open Directory Project directories.
Taxonomies
Finally, the Taxonomies provide us with a graphical representation of the distribution of the pages and the link between them within the domain.
How to export the report to PDF?
The SEO Spider is a very powerful tool and also allows you to “photograph” the status of the SEO to be able to send it to your client or your collaborators.
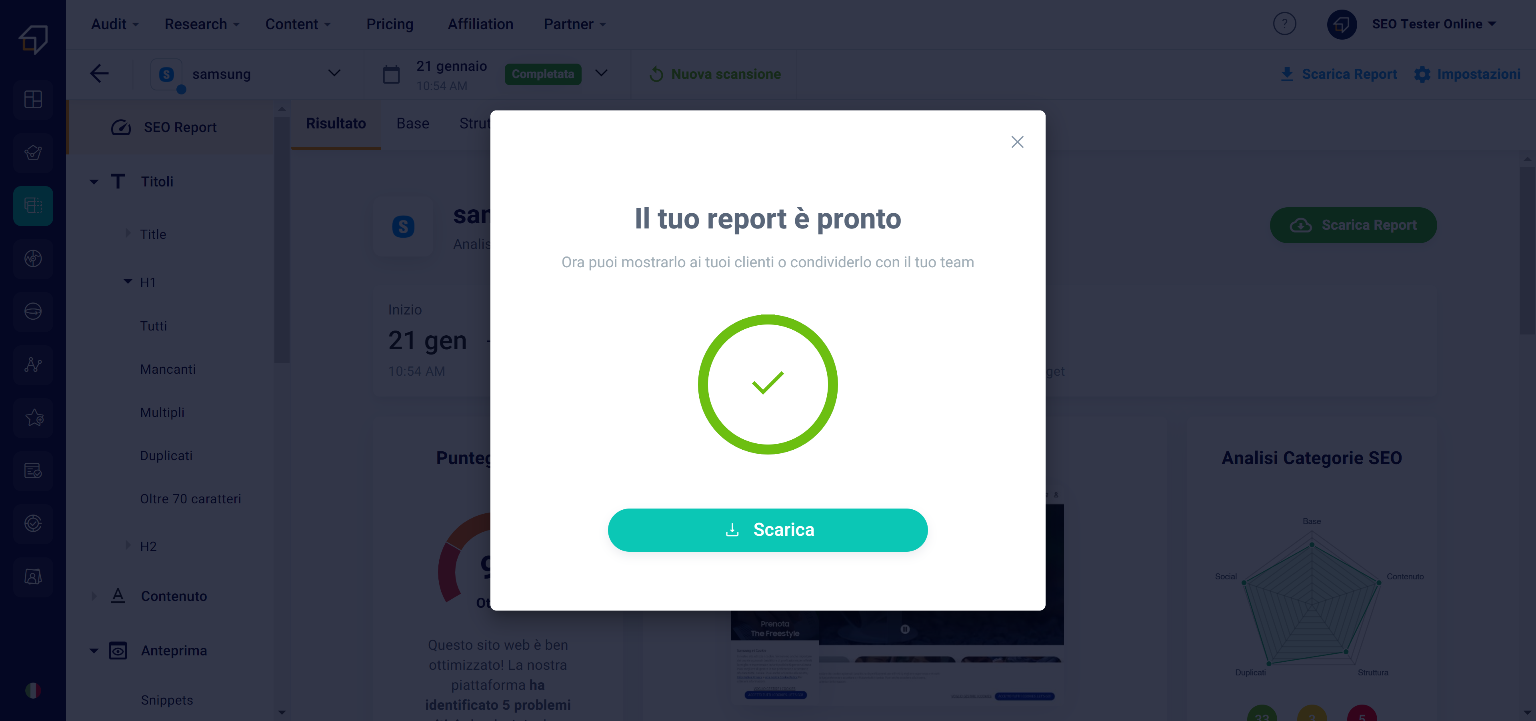
In fact, at the top right of any screen of the tool there is the “Download Report” button.
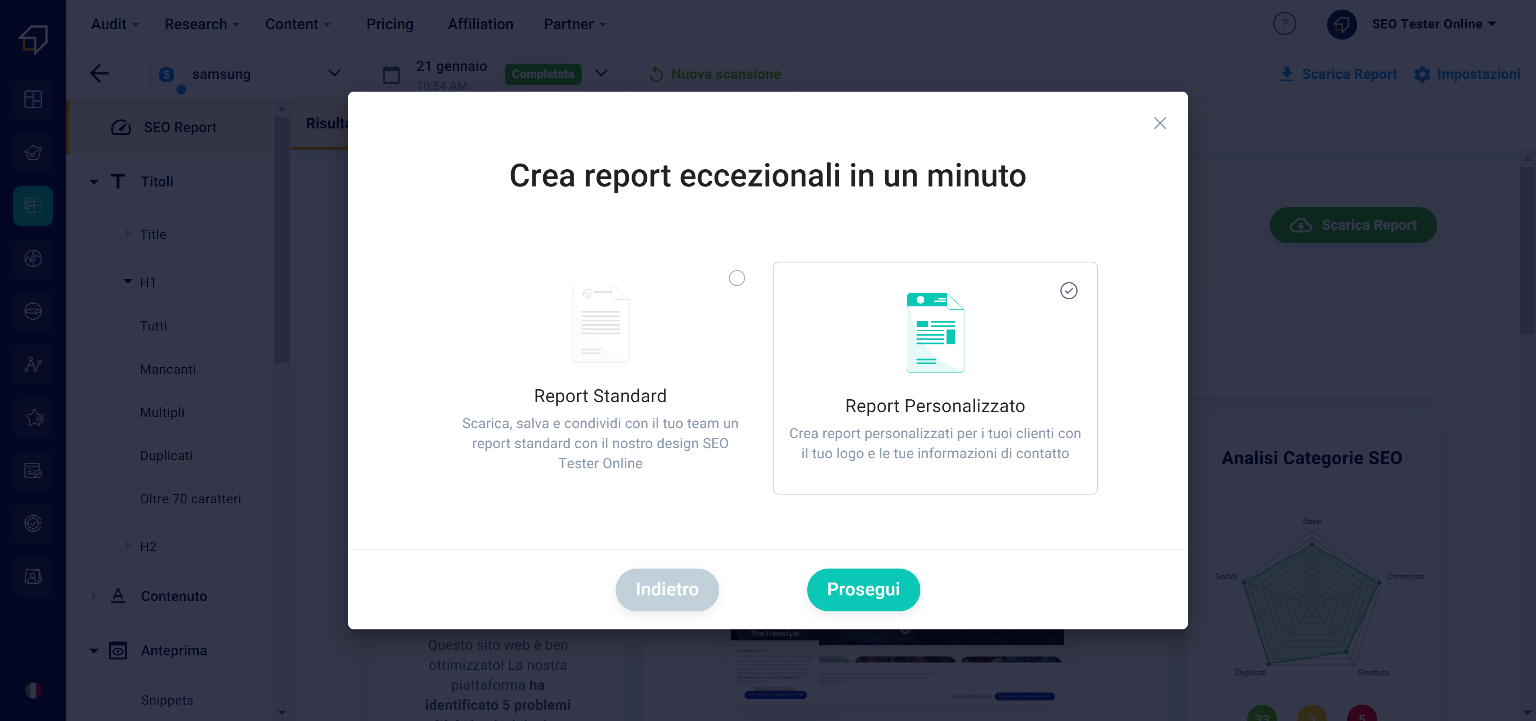
By clicking on this button, you can choose to create a standard report or a “White label report”, that is, customized with your logo and company information.
If you choose the standard report, click the “Download” button at the bottom right. It will take a few seconds to prepare it.
Once ready, you can save it to your computer by clicking on the “Download” button.
What will be downloaded will be a .pdf document in which you will find all the information of the various sections of the tool, including the aspects to improve and advice on how to do it. This report features the SEO Tester Online logo and contact information
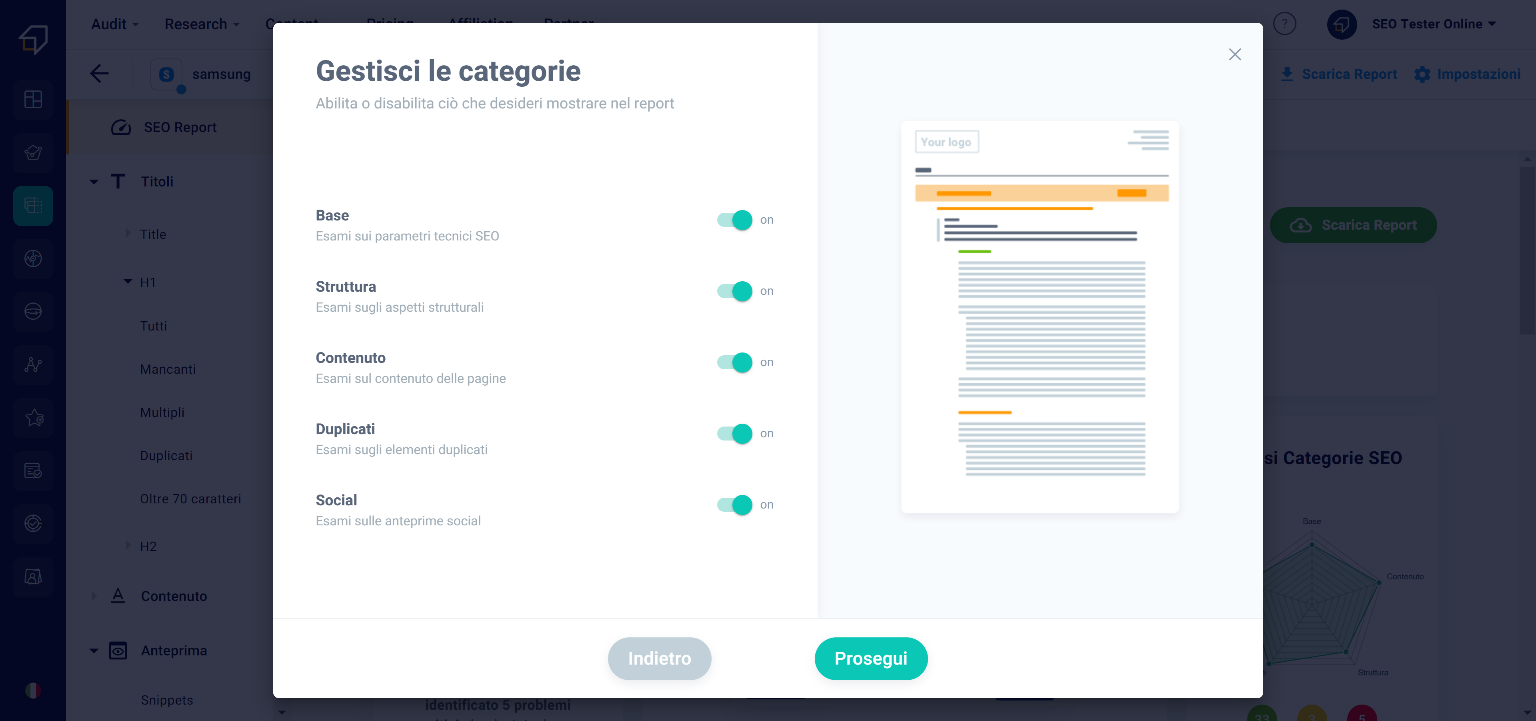
If you choose the white label custom report instead, you will need to add some information first. First, click on the “Continue” button.
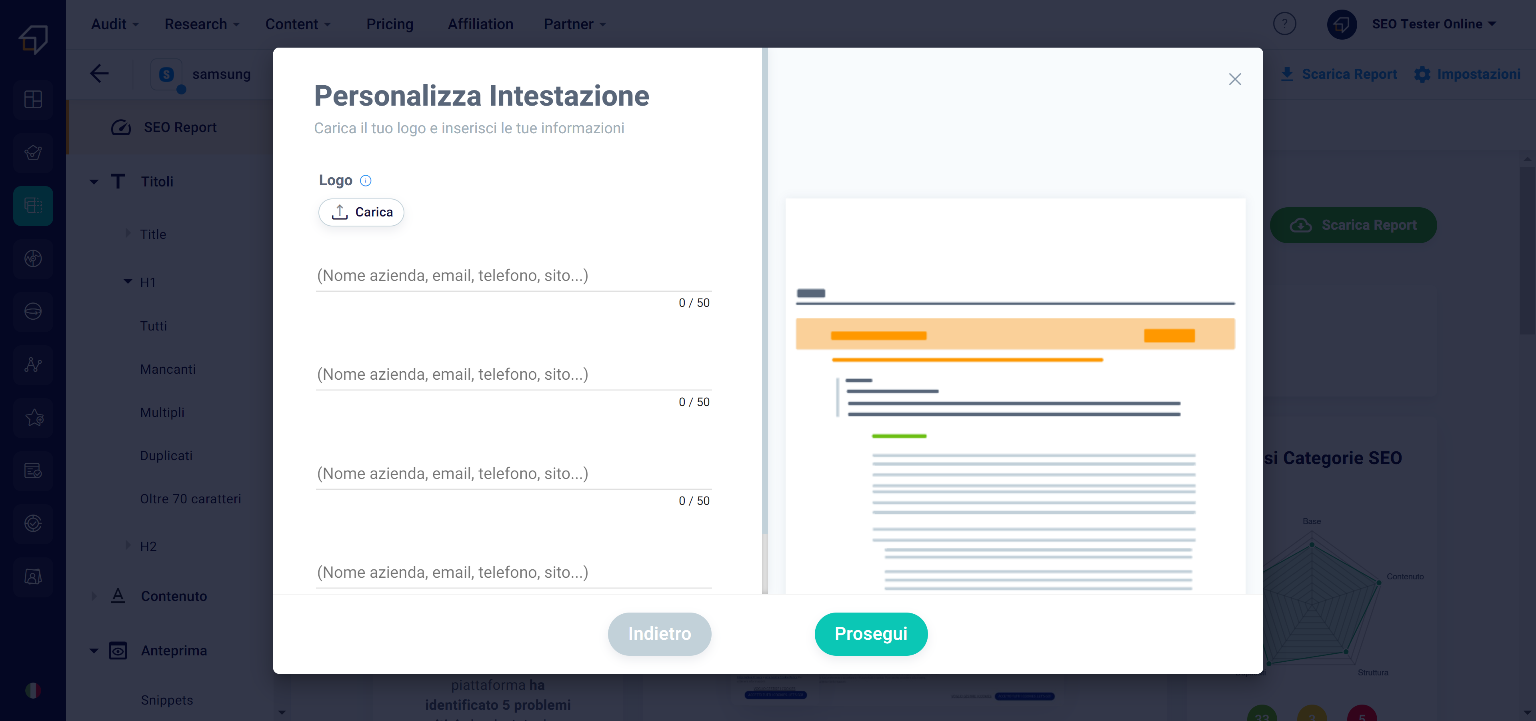
In the new window you will have to upload your company logo and the information you want to appear in the header of the report.
Subsequently, after clicking on the “Continue” button, thanks to the “On-Off” selectors you can decide which types of information to show in the PDF.
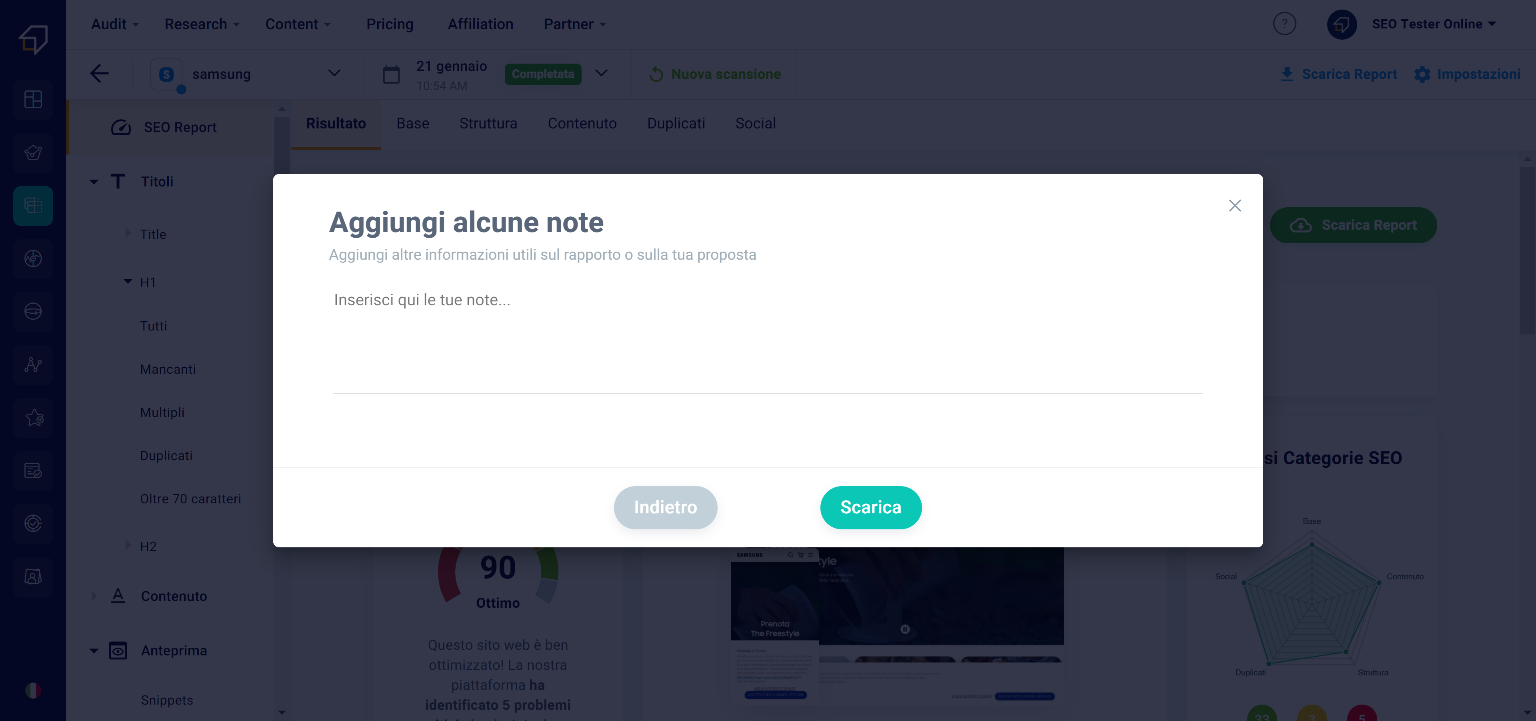
Finally, you can add notes using the text editor.
Then click on the “Download” button. The download will start in a short time!