The complete Guide to Google My Business
In this article, we will dive into Google My Business, a great ally to your local SEO. You will discover what it is, how does it work, and how to set-up and optimize your business’s listing.
What is Google My Business?
Google My Business is a free tool for local businesses. Thanks to it, people searching for products or services in your area can find your shop, organization or business, comprised of all the information they need.
In other words, it is the tool to manage your online presence on Google and a great way to interact with your customers.
How does Google My Business work?
On your side, you’ll have to set up an account, verify it, and add as much information you can about your business (location, opening hours, contacts, photos.)
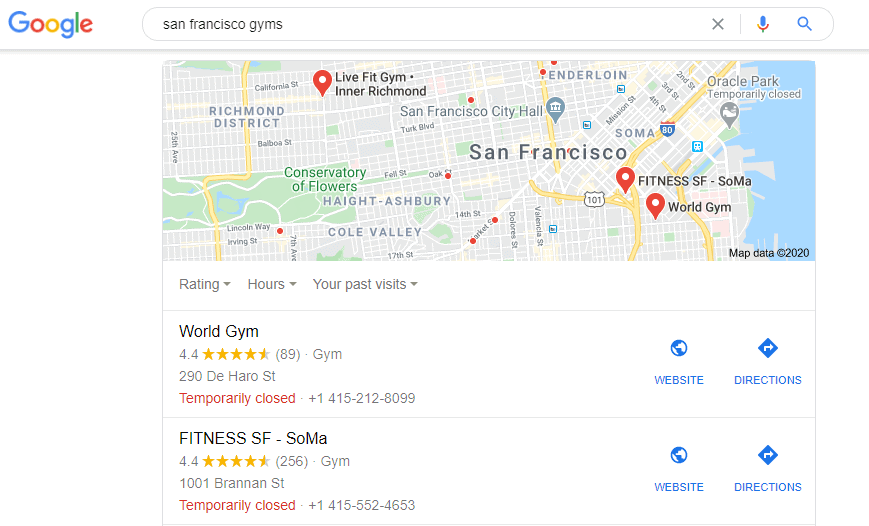
The user, instead, will see the information you added – plus things like reviews by other users – in a listing. The listing is that portion of the SERP on the right side.
It appears when someone performs a local search, something like “San Francisco gyms”
How to create a listing on Google My Business
First, you have to add your business’s profile on Google My Business.
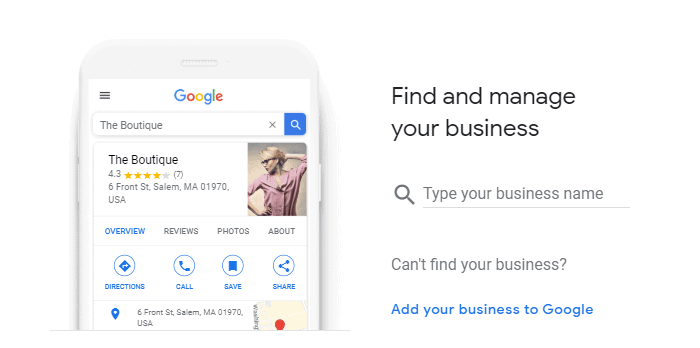
Insert the name, then the industry. You can choose whether adding a physical location or not. Whatever the nature of your business, we advise you to do it, it will boost your SEO. So, add the address.
Finally, tell people how to contact you. You can add both a phone number and the URL of your website.
Choose whether you want to get Google My Business’s newsletter or not, and you’re all set. Click on “Done”.
Now you must let Google verify that the contact information you put is correct and you’re the real owner of the business.
How to verify a location on Google My Business
Based on the nature of your business, you can choose among a variable number of choices. Please notice that you may not have all the options. You can also have only one.
By mail
You can decide to receive a postcard to your address.
It contains a confirmation code.
- Check if the address you inserted is correct;
- Add the (optional) contact name and click on the send button;
- Once you got it in your mailbox, go to the Google My Business homepage or open the mobile app;
- Click on verify location and then on verify now;
- On the code field, insert the five-digits code and click on the send
By phone
You can also use your phone for faster verification. You’ll receive an automated phone call to the number you used when you created your business’s profile. Of course, you need to keep your phone close. Log in to Google My Business or use the app, then click on the Verify now button;
- Select verify by phone, or call me now if you’re using the app;
- Wait for the call, then enter the code you hear.
By email
If your business typology allows it, you can choose to verify your location via email.
- Log in to Google My Business or use the app, then click on the Verify now button;
- Choose email among the options, or tap on the Send Email button if you’re using the app;
- Check your email and take note of the code;
- Click on the Verify button in the email message. If you’re doing this using the mobile app, tap on the Enter code button, enter the code and then tap on Submit.
Instant verification
This option is available only for a few businesses. You need to verify your website on Google Search Console first. If you used the same email address to sign into Google My Business and Search Console, go to Google My Business and do the verification.
What if you lost your code?
Just log in and select Request another code on the top of the page.
How to optimize your Google My Business listing
Once you’ve finished setting up the account and asking for verification, it is time to build your listing and add as much information as you can.
Even if you haven’t verified the listing already, you could begin adding all the information. Of course, the much information you add, the more you optimize your listing, and the more your local SEO will benefit.
The information you add will appear both on the SERP (on your listing) and on Google Maps.
Log in to Google My Business and select the listing you want to optimize.
On the home page, you have an overview of the information you can add, manage the users’ reviews and photos, create a post and other things. On the left menu, you can access specific sections. We will dive into the most important ones for the optimization of your listing:
Posts
Regular posting is a great way to tell Google that your business is active and up to date. Also, it is perfect to interact with your customers. To create a post, click on the corresponding item on the menu, then choose the type you want to create:
- Update: Tell your users what’s new with a post. You can also add a call to action button for more engagement.
- Product: You can highlight a new or a popular product, add pictures, price and description.
- Offer: you can tell your customers about a special sale, add an image, set the start and end dates, price, coupons and terms and conditions.
- Event: let people know about events regarding your business or your products. Add a picture, start and end dates and a description. You can also add an optional call to action button.
Info
You can add more information about your business or edit the pieces you entered when you set up the account.
The additional information you can enter comprises:
- Service area: the geographical locations you can reach with your products or services;
- Opening hours;
- A description: be extra careful with it. Make it very accurate and add the most relevant keywords.
- Other information: you can also put additional pieces of information by selecting the corresponding item on the left menu. These are:
Reviews
You should know how crucial it is for Google the usefulness of content. So, SEO-wise, reviews are essential. On Reviews, you can see what people have to say about you and answer them. Dealing with a negative review can make a difference with the crawler and other people, too.
Questions
The easier you are to reach, the better it is for SEO and your business. You can enable a live chat service for your customers. You will receive the messages on the app installed on your phone.
Products
Click on Get started. You can add photos, prices, a description, and a call to action button so your customers can discover and buy them directly from the SERP.
Services
Here you can be more specific about your business does. In addition to the more general industry, you can write about your activities in detail. To add a new service, click on + add another service. You can also add a price and a description of your services. Click on the pencil on the right of every item.
Questions and Answers
Once your listing is up and running, people can ask questions to you from the SERP by clicking on the Ask a question button. You can answer them, showing that you are active and attentive with your customers. Also, you can choose the most relevant question to show as firsts on the listing.
Photos
Images are the first things that strike your customer’s attention. You can add your logo, pictures of your products, and your shop, both inside and outside.
Also, you can choose to show some pictures taken by your customers.
Insights
Unlike other items, this is for your eyes only. Here you can discover who the people that interact with your listing are and get valuable information about your target.
What are some alternatives to Google My Business?
Being easy to find on Google with detailed information on your business is vital because Google is the most used platform to find information. But it is not the only one.
We advise you to have a look at tools that are similar to Google My Business. These are:
- Bing Places for Business, the Microsoft counterpart;
- Yahoo listings for small businesses: The Yahoo!’s equivalent.
- Facebook Pages. Why? Think about it: On Google My Business, you can add information and opening hours, add events, locations, products, photos, manage reviews. You can do these things on your Facebook Page, too. Facebook is another immensely used and populated platform, and having a Facebook Page helps your Google ranking, also. So, why don’t you take advantage of it?
Do you want to learn more about Local SEO?
Local SEO can produce a great competitive advantage for your business. If you wanna get deep on this topic, we suggest you to read our Introductive Guide to Local SEO.